A Helm downloader plugin that supports different file manipulations, conversions, encoders and decoders.
Table of contents
Quick start
If you think you are experienced enough and you just want to start using this plugin as soon as possible - here are some quick tips to get you started. For more detailed explanation of plugin itself please refer to specific chapters below.
Installation
helm plugin install https://github.com/true-north-engineering/helm-file-utils.git
Usage
helm install [NAME] [CHART] [flags] -f futl://path/to/values.yaml
Input example
#values.yaml
example_file:
- name: example_file
file: !futl base64dec+yaml2json+base64enc+file://files/example_file.yaml
#example_file.yaml
yaml_file:
- just_example
- just to demo it
Output example
example_file:
- name: example_file
file: |-
{
"yaml_file": [
"just_example",
"just to demo it"
]
}
Installation
After installing Helm, simply run the following:
helm plugin install https://github.com/true-north-engineering/helm-file-utils.git
For installing a specific release version (e.g. 0.1.0) please use following syntax:
helm plugin install https://github.com/true-north-engineering/helm-file-utils.git --version 0.1.0
Helm file utils also supports different architectures on different operating systems. Let’s say you only want to download specific version and architecture for specific OS. You can do so by providing adequate version, OS and architecture to the template below.
https://github.com/true-north-engineering/helm-file-utils/releases/download/v{version}/helm-file-utils_{version}_{os}_{architecture}.tar.gz
In the template above version represents one of the releases, OS one of the targeted operating systems - darwin, linux, windows, and architecture one of the supported architectures - 386, amd64, arm, arm64.
curl -sSL https://github.com/true-north-engineering/helm-file-utils/releases/download/v0.1.3/helm-file-utils_0.1.3_linux_amd64.tar.gz
To find more about specific releases please refer to github releases.
Usage and examples
Helm File Utils allows user to do multiple transformations over given file.
This plugin is only applicable to the -f or --values option of a Helm
command (e.g. install, upgrade or template). The basic usage
is to reference a directory (either absolutely, or relative to the
PWD) from which to collect all non-hidden files with the extension
.yaml or .yml, not including sub-directories. Keyword used to
associate plugin with given file directory is futl.
Basic usage of plugin is as it follows:
helm install [NAME] [CHART] [flags] -f futl://path/to/values.yaml
File transformations
In given .yaml or .yml file, multiple file transformations are possible.
Transformations are classified in two categories - Transformers(T) and Readers(R). Template for chaining
file transformations is !futl T+R://path/to/transform where every transformation needs to consist of at most
one Reader and any number of Transformers separated with + sign.
Order of transformation evaluation is from right to left, which forces Reader to always execute first.
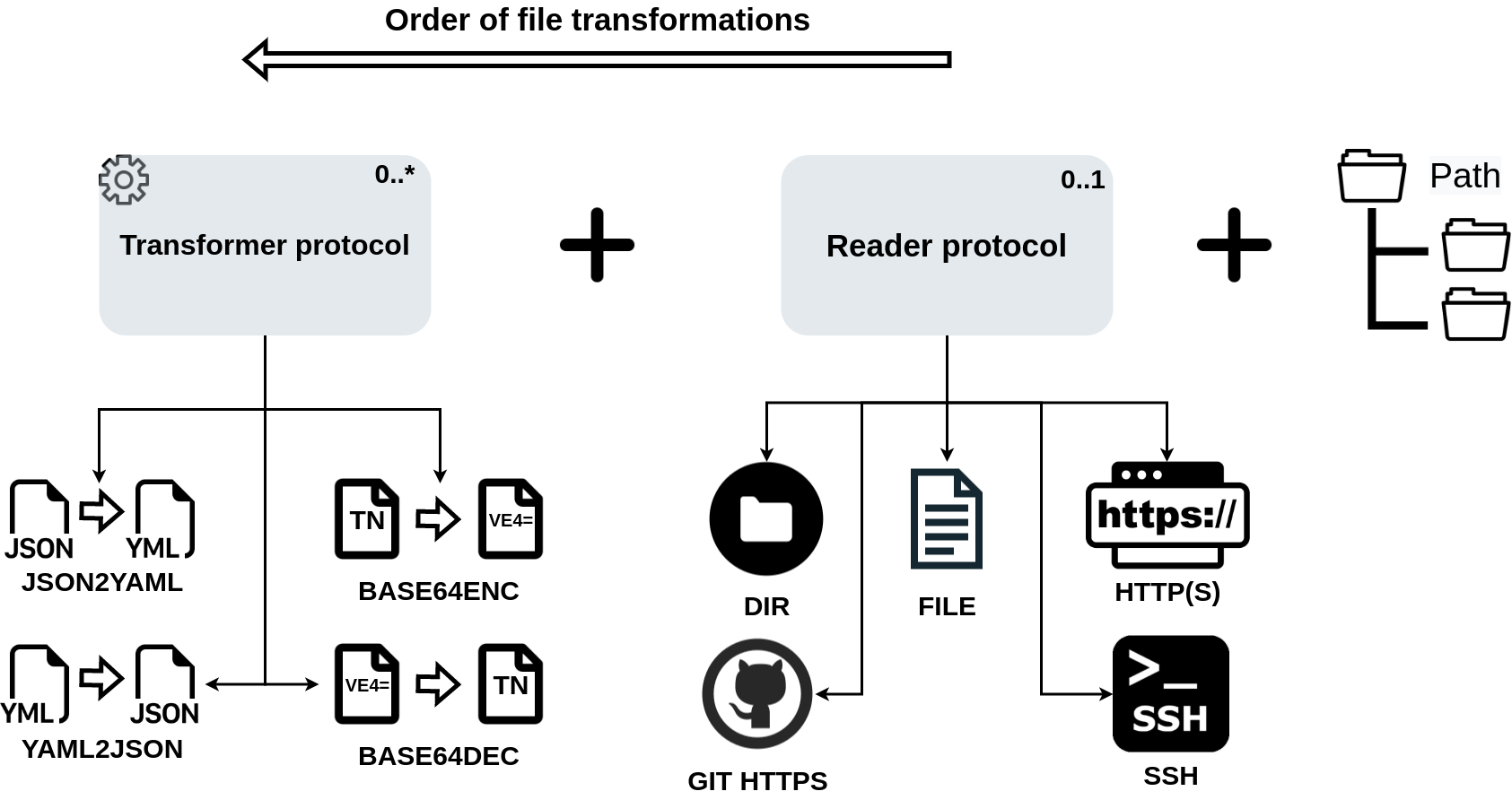
Readers
Used for reading the content from given destination. If none is provided, file is considered as default.
Available Readers are: file, dir, https, git_https, ssh
You can find detailed explanation of every available Reader followed by examples down below.
File
Default reader protocol that reads content from a single file no matter the extension.
!futl file://../directory/inputfile.txt
!futl ../directory/inputfile.txt
Dir
Protocol that reads content of provided directory.
!futl dir://../directory
Http(s)
Protocol that reads content of provided https url. It acts similarly to file reader as input is response body from url that is provided.
!futl https://path.to/read/input.txt
Git_https
Protocol that allows user to read content via git. Content is read from repository that can be either private or public one.
While public repositories require no authentication to acces the repository, private repositories require authentication
using username and password (Personal Access Token).
Order for checking credentials is as it follows:
- Check if credentials are provided in URI using the
[username[:password]@]syntax - Look for environment variables named FUTL_GIT_USER or FUTL_GIT_PASSWORD
- Look for environment variable named FUTL_CI - if variable exists prompt user to enter credentials
NOTE : It is assumed that environment variables are set by user himself otherwise program might not work as expected.
Git_https template followed by every field explanation can be found below. Optional fields are enlisted in [ ].
!futl git_https://[username[:password]@]git_clone_url path/to/read[#branch]
Credentials - optional field, allows user to authenticate when using the private repository as mentioned above
Git_clone_url - clone url of repository, e.g. github.com/true-north-engineering/helm-file-utils.git
Path - path to file or directory
Branch - optional field, can be used for fetching data from specific branch, if none is provided, default repository branch is used
Example of simple usage:
!futl git_https://true-north:pat@github.com/true-north-engineering/helm-file-utils.git tests/filetest/inputfile3.txt#develop
More examples of using git_https can be found in git_https test folder.
Ssh
Protocol that allows user to read content via ssh. To use the ssh it is required to have authentication.
Order for checking authentication is as it follows:
- Check for public keys stored in
path/from/home/variable/.ssh/.pubwhere path is assumed to be environment variable HOME - Check if credentials are provided in URI using the
[username[:password]@]syntax - Look for environment variables named FUTL_SSH_USER or FUTL_SSH_PASSWORD
- Look for environment variable named FUTL_CI - if variable exists prompt user to enter credentials
Ssh template followed by every field explanation can be found below. Optional fields are enlisted in [ ].
ssh://[username[:password]@]hostname[:port]/path/to/file
y
Credentials - optional field, allows user to authenticate when connecting via ssh
Hostname - host where ssh is hosted, can be IP or domain name
Port - optional field, allows user to change port where ssh is hosted, if not provided, default is 22
Path - path to file or directory\
More examples of using ssh can be found in ssh test folder.
Transformers
Transformers are used to do various transformations over the file.
Available Transformers: base64enc, base64dec, yaml2json, json2yaml
You can find detailed explanation of every available Transformer followed by examples down below.
Base64enc
Transformer that encodes given data into base64 standard.
!futl base64enc://../../tests/filetest/inputfile.txt
Base64dec
Transformer that decodes given base64 encoded data into string format.
!futl base64dec://../../tests/filetest/inputfile.txt
Yaml2json
Transformer that transforms given .yaml or .yml file into .json file.
!futl yaml2json://../../tests/filetest/inputfile_yaml.yaml
Json2yaml
Transformer that transforms given .json file into .yaml file.
!futl json2yaml://../../tests/filetest/inputfile_json.json
Examples
helm install [NAME] [CHART] [flags] -f futl://home/usr/files
* home
* usr
* files
* values.yaml
* charts
* chart.yaml
#values.yaml
#default reader is file so having "file" listed as reader is deprecated
example_file:
- name: example_file
file: !futl base64enc://example_file.txt
#since we are iterating over dir, reader of type "dir" is needed
example_dir:
- name: example_dir
file: !futl base64enc+dir://example_dir
#Chart.yaml
#this is just an example of a simple Chart file that is provided
apiVersion: v1
appVersion: "1.0"
description: Deploy a basic Chart Config Map
home: https://helm.sh/helm
name: example_chart
sources:
- https://github.com/helm/helm
version: 0.1.0
For more examples please visit this page or even better - check tests folder.
Issues
Contribution guide
Contributions are more than welcome. If you would like to contribute to this plugin please see these instructions that will help you to develop the plugin.
